FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Fund Flow Analysis
Part A: Discussion of basic theories including various methods and techniques of preparing the Funds Flow Statement and explanation of important definitions and points relevant to analysing the funds flow of a business enterprise effectively in order to preparing the Funds Flow Statement most appropriately.
Part B: 7 Illustrations with solutions
Part A
Definitions
Fund is the other name of working capital.
We know that working capital is the excess of the
value of current assets (including loans and advances) over the value of
current liabilities (including provisions). Therefore, fund can
also be defined as the capital which is not fixed and which is required for
running the business operations on day to day basis.
Fund flow implies the difference between the opening balance and the
closing balance of fund with respect to an accounting year.
If the closing balance of fund is less than the opening balance, it can be
termed as outflow of fund over the
period of the accounting year. On the other hand, if the closing balance of fund
is more than the opening balance, it can be termed as inflow of fund.
Fund flow analysis implies a systematic analysis of the fund flow to
identify the reasons of increase or decrease in the balance of fund over the
period of the accounting year.
Technique of fund flow analysis
Technique
of fund flow analysis involves following three steps:
1. Preparation of statement showing computation of funds from operations;
2. Preparation of statement showing changes in working capital; and
3. Preparation of funds flow statement.
Step: I
Preparation of statement showing computation
of funds from operations
Funds from operations can be computed either in direct method or in indirect method.
Direct method:
Statement
showing computation of funds from operations
|
|
Particulars |
Rs |
Rs |
|
|
Sales |
|
××× |
|
LESS |
Raw
materials consumed |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Power
and fuel |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Wages,
salaries and bonus |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Workmen
and staff welfare expenses |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Repairs
and maintenance |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Brokerage
and commission |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Insurance
premium |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Rent,
rates and taxes |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Contribution
to provident fund |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Contribution
to superannuation fund |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Pension
and gratuity |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Research
and development |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Travelling
expenses |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Directors’
fees |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Audit
fees |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Turnover
tax |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Sales
tax |
××× |
××× |
|
|
Funds from
operations |
|
××× |
Note:
Items
like depreciation, provision for bad and doubtful debts, losses and gains of
non-trading nature, write offs, interest on debentures and loans, etc. are not
to be considered while calculating the funds from operations under direct
method.
Indirect method:
Statement
showing computation of funds from operations
|
|
Particulars |
Rs |
Rs |
|
|
Net
profit for the year ended.........(as per the balance sheet) |
|
××× |
|
ADD |
Transfer
to General Reserve, DRR, W C Reserve |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Proposed
dividend of current year (if appears in balance sheet) |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Interim
dividend paid |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Preference
dividend paid |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Provision
for tax (provision made during the current year) |
××× |
××× |
|
|
Net profit before tax |
|
××× |
|
ADD |
Depreciation
on fixed assets |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Loss
on sale of fixed assets |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Goodwill
written off |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Preliminary
expenses written off |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Interest
on debentures, loans and public deposits (treated
as non-operating expense) |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Loss
on sale of long term investments |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Discount
on issue of shares/debentures written off |
××× |
|
|
ADD |
Premium
on redemption of debentures/ preference shares |
××× |
××× |
|
|
|
|
××× |
|
LESS |
Profit
on sale of fixed assets |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Profit
on sale of long term investments |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Dividend
on investments in shares |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Interest
on investments in debentures |
××× |
|
|
LESS |
Discount
on redemption of debentures/ preference shares |
××× |
××× |
|
|
Funds from
operations |
|
××× |
Step: II − Preparation of statement showing
changes in working capital
Statement
showing changes in working capital
|
Particulars |
Previous
Year (Rs) |
Current
Year(Rs) |
Increase
in W.C. (Rs) |
Decrease
in W.C. (Rs) |
|
Current Assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
Closing
stock (net of provision) |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Sundry
debtors (net of provision) |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Marketable
securities (short-term
investments) |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Accrued
incomes |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Cash
at bank / hand |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Loans
and advances |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Bills
receivable |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Prepaid
expenses |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
TOTAL (A) |
××× |
××× |
|
|
|
Current Liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
Sundry
creditors |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Bills
payable |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Outstanding
expenses |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Incomes
received in advance |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
Bank
overdraft |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
TOTAL (B) |
××× |
××× |
|
|
|
Working
Capital (A – B) |
××× |
××× |
|
|
|
Increase / Decrease in W.C. |
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
|
|
××× |
××× |
××× |
××× |
Step: III − Preparation of funds flow
statement
Funds flow
statement for the year ended........................
|
Sources |
Rs |
Applications |
Rs |
|
Funds
from operations |
××× |
Funds
lost in operations |
××× |
|
Issue
of share capital |
××× |
Redemption
of preference shares |
××× |
|
Issue
of debentures |
××× |
Redemption
of debentures |
××× |
|
Raising
other long term loans |
××× |
Repayment
of long term loans |
××× |
|
Sale
of fixed assets |
××× |
Buy-back
of equity shares |
××× |
|
Sale
of investments |
××× |
Purchase
of fixed assets |
××× |
|
Dividend
received |
××× |
Purchase
of investments |
××× |
|
Interest
received |
××× |
Payment
of proposed dividend of previous year |
××× |
|
Decrease
in working capital |
××× |
Payment
of interim dividend |
|
|
|
|
Payment
of interest (treated
as non-operating expense) |
××× |
|
|
|
Payment
of tax (treated
as non-current item) |
××× |
|
|
|
Increase
in working capital |
××× |
|
|
××× |
|
××× |
Some Important Points / Explanations:
1. Current Investments
Current investments are considered as part of working capital.
2. Treatment of bank overdraft and cash credit
Bank overdraft and cash credit are to be treated as short-term
borrowings and should be considered as part of current liabilities.
3. Provision against current assets
Very
often provision is made for doubtful debts and obsolescence or loss in the
value of inventory. In such cases the concerned item of current
asset should be shown net of provision in the “Statement showing changes in
working capital”.
4. Treatment of bad debts
Bad
debts written off during the year may be added
back to the closing balances of provision for doubtful debts and trade
receivables. Alternatively,
the adjustment of writing off of bad debts may be ignored and
the solution can be given on the basis of the closing balances of provision for
doubtful debts and trade receivables as appearing in the balance sheet without
adding back the bad debts written off during the year to the said closing
balances.
5. Purchasing a business by issue of fully paid shares
If
assets and liabilities of another company are purchased by issuing fully paid
shares, the entire amount of issue of shares
against the business purchase should be shown as source of fund and acquisition of fixed assets should be
shown as application of fund. The “Statement showing changes in working
capital” will be prepared as usual.
6. Treatment of proposed dividend
(a) Dividend proposed for the previous year will be an application of fund, unless otherwise stated, on the assumption that the proposed amount has been approved by the shareholders in the AGM.
(b) No effect is given to Proposed Dividend for the current year as it is not provided for and is a contingent liability.
(c)
Any unpaid dividend is transferred to Dividend Payable
A/c / Unpaid Dividend A/c which is shown in the Balance Sheet of the current
year as Other Current Liabilities under Current Liabilities.
7. Interest on debentures and loans
As
advocated by The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) in AS3 – Cash Flow Statement, it has to be
added back in the “Statement showing computation of funds from operations” and
then payment of interest has to be shown as application of fund in the “Funds
flow statement”.
8. Unclaimed dividend
It
is the dividend which could not be distributed by the company due to shareholders’
indifference such as non-presenting the dividend warrant to bank or change of address
without intimation to the company, etc. In the balance sheet unclaimed dividend
is shown under the head “Current Liabilities” so long as it is not claimed.
Like
proposed dividend, unclaimed dividend can also be treated either as current
liability or as noncurrent liability. If
it is treated as current liability, it will be shown in the “Statement showing
changes in working capital” like other current liabilities. In that case, no
further treatment will be required for this, either in the “Statement showing
computation of funds from operations”, or in the “Funds flow statement”.
If unclaimed dividend is treated as non-current liability,
it will not be shown in the “Statement showing changes in working capital”. In
this case, there may be two different situations
requiring two different accounting treatments.
Situation: I
If the balance of unclaimed dividend at the end of the current year is more than the balance at the end of the previous year, the amount of increase will be transferred to the proposed dividend account by making the following journal entry:
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit (Rs) |
Credit (Rs) |
|
|
Proposed
dividend A/c Dr |
|
|
|
|
|
To Unclaimed dividend A/c |
|
|
|
|
|
(Increase
in unclaimed dividend during the current year transferred to Proposed
Dividend Account) |
|
|
|
Under
this situation, the amount of proposed dividend (of the previous year) paid
during the current year will be assumed to be the amount as reduced by the
amount of increase in the balance of unclaimed dividend.
Situation: II
If the balance of unclaimed dividend at the end of the current year is less than the balance at the end of the previous year, the amount of decrease will be assumed to be the amount of unclaimed dividend (of the previous year) paid during the current year. The necessary journal entry made for such payment of unclaimed dividend was:
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit (Rs) |
Credit (Rs) |
|
|
Unclaimed
dividend A/c Dr |
|
|
|
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
|
|
(Amount
of unclaimed dividend of the previous year paid during the current year) |
|
|
|
9. Goods lost in transit
It
is an abnormal (i.e. non-operating) event. So it has to be added back in the
“Statement showing computation of funds from operations”. Then it has to be
shown as application of fund in the “Funds flow statement”.
Part B
Illustration: 1
From the following Balance Sheets of
Priceless Ltd. prepare Funds Flow Statement for the year 2016.
Balance sheets as at (Rs in ’000)
|
Liabilities |
31.3.15 |
31.3.16 |
Assets |
31.3.15 |
31.3.16 |
|
Equity sh. capital |
150 |
200 |
Goodwill |
50 |
40 |
|
9% Red. Pref. sh. cap |
75 |
50 |
Land & Building |
100 |
85 |
|
Capital Reserves |
- |
10 |
Plant & Machinery |
40 |
100 |
|
General Reserves |
20 |
25 |
Investments |
10 |
15 |
|
P/L Account |
15 |
24 |
Debtors |
70 |
85 |
|
Proposed Dividend |
21 |
25 |
Stock |
39 |
55 |
|
Creditors |
13 |
24 |
Bills Receivable |
10 |
15 |
|
Bills Payable |
10 |
8 |
Cash in hand |
7 |
5 |
|
Liability for Expenses |
15 |
18 |
Cash at bank |
5 |
4 |
|
Provision for tax |
20 |
25 |
Preliminary Expenses |
8 |
5 |
|
|
339 |
409 |
|
339 |
409 |
Additional information:
1. A part of land was sold out in
2016, and the profit was credited to Capital Reserve.
2. A machine has been sold for Rs 5,000
(written down value of the machinery was Rs 6,000). Depreciation of Rs 5,000
was charged on plant in 2016.
3. An interim dividend of Rs 10,000
has been paid in 2016.
4.
An Amount of Rs 1,000 has been received as dividend on
investment in 2016.
Solution: 1
Illustration: 2
The Balance Sheets of Pinnacle
Corporation as at the end of 2015 and 2016 are given below:
|
Liabilities |
2015
(Rs) |
2016
(Rs) |
Assets |
2015
(Rs) |
2016
(Rs) |
|
Share capital |
1,00,000 |
1,50,000 |
Freehold land |
1,00,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
Share premium |
- |
5,000 |
Plant at cost |
1,04,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
General Reserves |
50,000 |
60,000 |
Furniture at cost |
7,000 |
9,000 |
|
P/L Account |
10,000 |
17,000 |
Investments |
60,000 |
80,000 |
|
6% Debentures |
70,000 |
50,000 |
Debtors |
30,000 |
70,000 |
|
Provision for dep. (on plant) |
50,000 |
56,000 |
Stock |
60,000 |
65,000 |
|
Provision for dep. (on Furniture) |
5,000 |
6,000 |
Cash |
30,000 |
45,000 |
|
Provision for taxation |
20,000 |
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
Creditors |
86,000 |
95,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,91,000 |
4,69,000 |
|
3,91,000 |
4,69,000 |
A plant purchased for Rs 4,000
(Depreciation provided Rs 2,000) was sold for Rs 800 on 30th
September, 2015. On 30th June, 2015 an item of furniture was
purchased for Rs 2,000. These were the only transactions concerning fixed
assets during 2015. A dividend of 22½ % on original shares was paid. You are
required to prepare funds Flow Statement and verify the results by preparing a
schedule of changes in Working Capital.
Solution: 2
Illustration: 3
From the Balance Sheet of
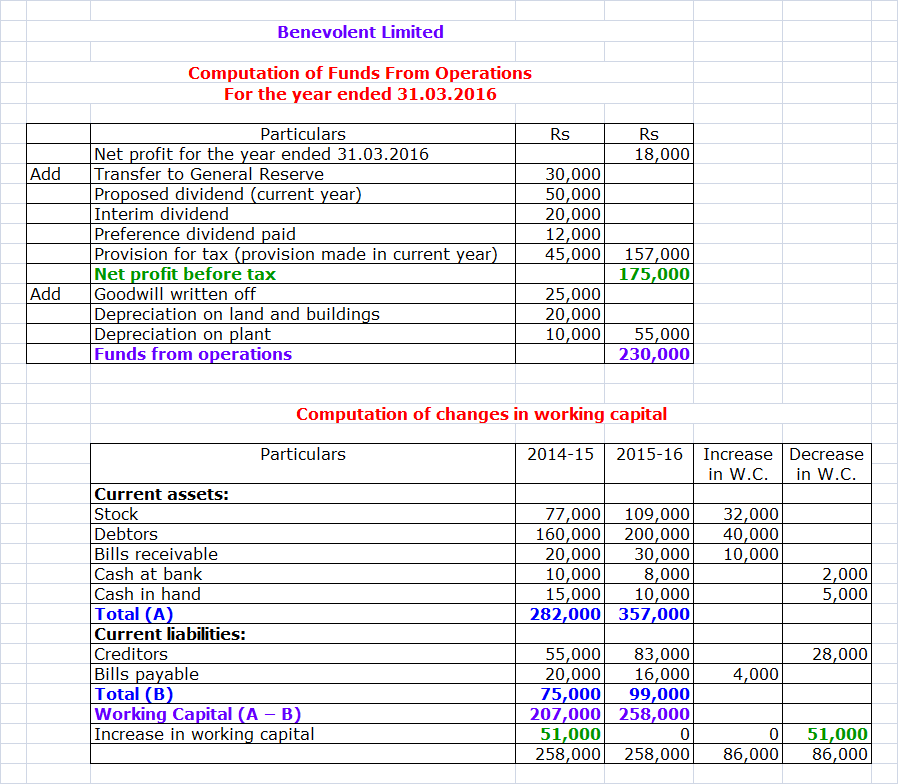
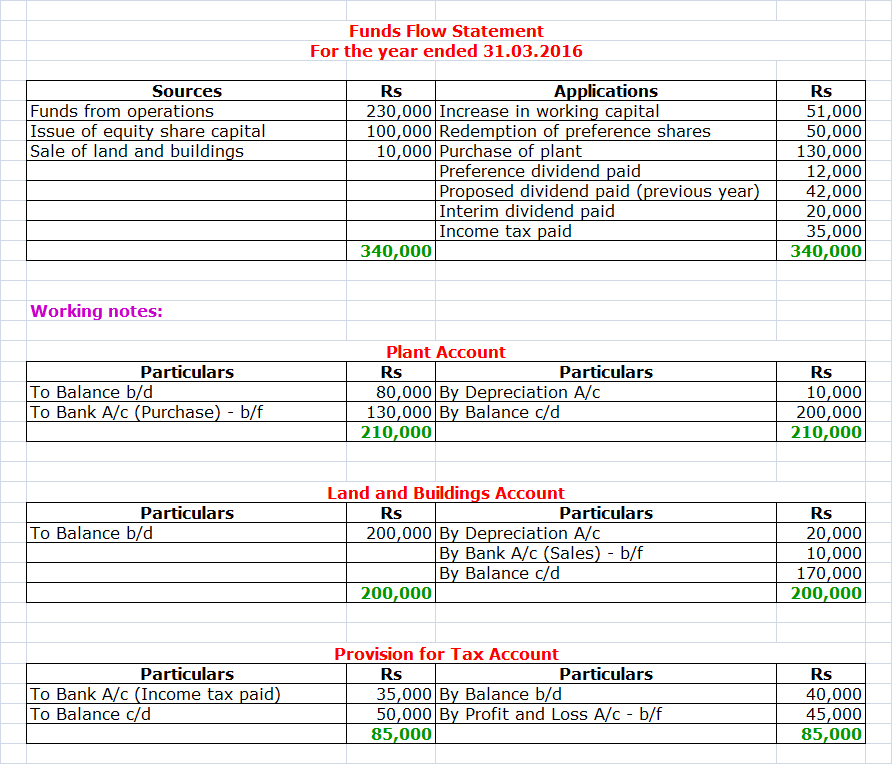
Benevolent Ltd., please prepare:
A. A Statement of changes in
the Working Capital.
B. Funds Flow Statement.
Balance Sheet at
|
|
31st
March |
|
31st
March |
||
|
Liabilities |
2015
(Rs) |
2016
(Rs) |
Assets |
2015
(Rs) |
2016
(Rs) |
|
Equity share capital |
3,00,000 |
4,00,000 |
Goodwill |
1,15,000 |
90,000 |
|
8% Pref. Sh. Cap. |
1,50,000 |
1,00,000 |
Land & Buildings |
2,00,000 |
1,70,000 |
|
P/L Account |
30,000 |
48,000 |
Plant |
80,000 |
2,00,000 |
|
General reserves |
40,000 |
70,000 |
Debtors |
1,60,000 |
2,00,000 |
|
Proposed dividend |
42,000 |
50,000 |
Stock |
77,000 |
1,09,000 |
|
Creditors |
55,000 |
83,000 |
Bills receivable |
20,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bills payable |
20,000 |
16,000 |
Cash in hand |
15,000 |
10,000 |
|
Provision for taxation |
40,000 |
50,000 |
Cash at bank |
10,000 |
8,000 |
|
|
6,77,000 |
8,17,000 |
|
6,77,000 |
8,17,000 |
Following is the additional information
available:
i.
Depreciation of Rs 10,000 and Rs 20,000 have been
charged on Plant and Land and Buildings respectively in 2016.
ii.
Interim dividend of Rs 20,000 has been paid in 2016.
iii.
Income tax of Rs 35,000 has been paid in 2016.
Solution: 3
Illustration: 4
From the following balance sheets of Reindeers Limited prepare a statement showing the changes in the Working Capital and Funds Flow Statement during the year 2015.
Balance sheet as at
|
|
Rs |
Rs |
|
Assets: |
31.12.2014 |
31.12.2015 |
|
Fixed assets (net) |
5,10,000 |
6,20,000 |
|
Investments |
30,000 |
80,000 |
|
Current assets |
2,40,000 |
3,75,000 |
|
Discount on debentures |
10,000 |
5,000 |
|
Total |
7,90,000 |
10,80,000 |
|
Liabilities: |
|
|
|
Equity share capital |
3,00,000 |
3,50,000 |
|
Preference share capital |
2,00,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
Debentures |
1,00,000 |
2,00,000 |
|
Reserves |
1,10,000 |
2,70,000 |
|
Provision for doubtful debts |
10,000 |
15,000 |
|
Current liabilities |
70,000 |
1,45,000 |
|
Total |
7,90,000 |
10,80,000 |
You are informed that during the year:
i. A machine costing Rs 70,000
book value Rs 40,000 was disposed of for Rs 25,000.
ii. Preference share redemption was
carried out at a premium of 5%, and
iii. Interim Dividend at 15% was
paid on equity shares for the year 2014.
Further:
1.
The provision for depreciation stood at Rs 1,50,000 on
31st December, 2014 and at Rs 1,90,000 on 31st December,
2015; and
2.
Stock which was valued at Rs 90,000 as on 31st
December, 2014 was written up to its cost Rs 1,00,000 for preparing Profit and
Loss account for the year 2015.
Solution: 4
Illustration: 5
The directors of Chintamani Ltd.
present you with the Balance Sheets as on 30th June, 2015 and 2016 and ask you to
prepare statements which will show them what has happened to the money which
came into the business during the year 2016.
Balance sheet as at
|
|
Rs |
Rs |
|
Liabilities: |
30.06.2015 |
30.06.2016 |
|
Authorised capital (15,000 shares
of Rs 100 each) |
15,00,000 |
15,00,000 |
|
Paid up capital |
10,00,000 |
14,00,000 |
|
Debentures (2016) |
4,00,000 |
- |
|
General Reserves |
60,000 |
40,000 |
|
P & L Appropriation A/c |
36,000 |
38,000 |
|
Proposed dividends |
78,000 |
72,000 |
|
Sundry creditors |
76,000 |
1,12,000 |
|
Bank overdraft |
69,260 |
1,29,780 |
|
Bills payable |
40,000 |
38,000 |
|
Loans on mortgage |
- |
5,60,000 |
|
Total |
17,59,260 |
23,89,780 |
|
Assets: |
|
|
|
Land and freehold buildings |
9,00,000 |
9,76,000 |
|
Plant and machinery |
1,44,000 |
5,94,000 |
|
Fixtures and fittings |
6,000 |
5,500 |
|
Cash in hand |
1,560 |
1,280 |
|
Sundry debtors |
1,25,600 |
1,04,400 |
|
Bills receivable |
7,600 |
6,400 |
|
Stock |
2,44,000 |
2,38,000 |
|
Prepayments |
4,500 |
6,200 |
|
Shares in other companies |
80,000 |
2,34,000 |
|
Goodwill |
2,40,000 |
2,20,000 |
|
Preliminary expenses |
6,000 |
4,000 |
|
Total |
17,59,260 |
23,89,780 |
You are given the following additional
information:
(a)
Depreciation has been charged (i) on Freehold
Buildings @ 2½% p.a. on cost Rs 10, 00,000. (ii) On Machinery and Plant Rs
32,000 (iii) on Fixtures and Fittings @5% on cost Rs 10,000. No depreciation
has been written off on newly acquired Building and Plant and Machinery.
(b)
A piece of land costing Rs 1, 00,000 was sold in 2016
for Rs 2, 50,000. The sale proceeds were credited to Land and Buildings.
(c)
Shares in other companies were purchased and dividends
amounting to Rs 6,000 declared out of profits made prior to purchase has
received and used to write down the investment (shares).
(d)
Goodwill has been written down against General
Reserve.
(e)
The proposed dividend for the year ended 30th
June 2015 was paid and, in additions, an interim dividend, Rs 52,000 was paid.
Solution: 5
Illustration: 6
The following is the Balance Sheets of the Android Industries Limited as at 31st December 2015 and 2016.
Balance sheet as at
|
|
Rs |
Rs |
|
Assets: |
31.12.2015 |
31.12.2016 |
|
Fixed assets: |
|
|
|
Property |
1,48,500 |
1,44,250 |
|
Machinery |
1,12,950 |
1,26,200 |
|
Goodwill |
- |
10,000 |
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
Stock |
1,10,000 |
92,000 |
|
Debtors |
86,160 |
69,430 |
|
Cash at bank |
1,500 |
11,000 |
|
Pre-payments |
3,370 |
1,000 |
|
Total |
4,62,480 |
4,53,880 |
|
Liabilities: |
|
|
|
Shareholders’ funds: |
|
|
|
Paid up capital |
2,20,000 |
2,70,000 |
|
Reserves |
30,000 |
40,000 |
|
Profit and loss A/c |
39,690 |
41,220 |
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
Creditors |
39,000 |
41,660 |
|
Bills payable |
33,790 |
11,000 |
|
Bank overdraft |
60,000 |
- |
|
Provision for taxation |
40,000 |
50,000 |
|
Total |
4,62,480 |
4,53,880 |
During the year ended 31st
December, 2016, a divided of Rs 26,000 was paid and assets of another company
were purchased for Rs 50,000 payable in fully paid-up shares. Such assets
purchased were:
Stock: Rs 21,640; Machinery: Rs
18,360; and Goodwill: Rs 10,000. In addition Plant at a cost of Rs 5,650 was
purchased during the year; depreciation on Property Rs 4,250; on Machinery Rs
10,760. Income tax during the year amounting to Rs 38,770 was charged to
provision for taxation. Net profit for the year before tax was Rs 76,300.
Prepare Funds Flow Statement for the
year 2016.
Solution: 6
Illustration: 7
The following are the Balance Sheets of Gamma Industries Limited for the year ending March 31, 2015 and March 31, 2016:
Balance sheet as at
|
|
Rs |
Rs |
|
Capital and liabilities: |
31.03.2015 |
31.03.2016 |
|
Share capital |
6,75,000 |
7,87,500 |
|
General reserves |
2,25,000 |
2,81,250 |
|
Capital reserve (profit on sale of
investment) |
- |
11,250 |
|
Profit and loss A/c |
1,12,500 |
2,25,000 |
|
15% Debentures |
3,37,500 |
2,25,000 |
|
Accrued expenses |
11,250 |
13,500 |
|
Creditors |
1,80,000 |
2,81,250 |
|
Proposed dividends |
33,750 |
38,250 |
|
Provision for taxation |
78,750 |
85,500 |
|
Total |
16,53,750 |
19,48,500 |
|
Assets: |
|
|
|
Fixed assets |
11,25,000 |
13,50,000 |
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation |
2,25,000 |
2,81,250 |
|
Net fixed assets |
9,00,000 |
10,68,750 |
|
Long- Term Investments (at cost) |
2,02,500 |
2,02,500 |
|
Stock (at cost) |
2,25,000 |
3,03,750 |
|
Debtors (net of provision for doubtful
debts of Rs 45,000 and Rs 56,250 respectively for 2015 and 2016) |
2,53,125 |
2,75,625 |
|
Bills receivable |
45,000 |
73,125 |
|
Prepaid expenses |
11,250 |
13,500 |
|
Miscellaneous expenditure |
16,875 |
11,250 |
|
Total |
16,53,750 |
19,48,500 |
Additional Information:
1.
During the year 2015-16, fixed assets with a net book
value of Rs 11,250 (accumulated depreciation, Rs 33,750) was sold for Rs 9,000.
2.
During the year 2015-16, Investments costing Rs 90,000
were sold, and also Investments costing Rs 90,000 were purchased.
3.
Debentures were retired at a Premium of 10%.
4.
Tax of Rs 61,875 was paid for 2015-16.
5.
During the year 2015-16, bad debts of Rs 15,750 were
written off against the provision for doubtful debts account.
6.
The proposed dividend for 2007-2008 was paid in
2015-16.
Required:
Prepare a Fund Flow Statement for the
year ended March 31, 2016.
Solution: 7













Very nice and helpful for my future exams.
ReplyDeleteThank you Utsav for your valuable comments. I am particularly happy to know that this article on Fund Flow Analysis helped you preparing for December, 2021 term exams.
ReplyDeletePlease keep on reading the articles published in this blog and upgrade your knowledge and concept about different topics of various subjects of your chosen courses. Of course, please don't forget to give your valuable comments after reading the articles.