Financial Accounting
Final Accounts of a
Non-Profit Organisation
Part A: Discussion of basic theories in regard to
methods of accounting for non-profit organisations including (1) definition,
meaning and accounting treatment of some important items like subscriptions,
entrance fees, donations, life membership fees, capital fund, etc., and (2) Format
of Subscription Account.
Part B: Eleven Illustrations with Solutions.
Introduction
Non-profit
organisation is an organisation which is set up for the benefit of the society
as a whole instead of for the benefit of any sole proprietor or any group of
partners or shareholders. Earning profit is not the motive of the non-profit
organisations rather their main objectives are providing social, educational,
religious or charitable benefits to the society at large. Examples of
non-profit organisation are club, charitable institution, charitable society,
charitable hospital, etc. Like any business organisation a non-profit
organisation also has to maintain its books of accounts throughout the
accounting year and at the end of the year has to prepare its own final
accounts.
Differences between a business
organisation and a non-profit organisation
The
major differences, from accounting point of view, between a business
organisation and a non-profit organisation are as follows:
1.
A business organisation is set up and exists for
earning profit, whereas a non-profit organisation is set up and
exists for rendering beneficial service
to the society without making any profit for any member of the organisation.
2. Final Accounts of a Business Organisation consist of trading account, profit and loss account and balance
sheet, whereas final accounts of a non-profit organisation
consist of receipts and payments account, income and
expenditure account and balance sheet.
3.
Profit and loss account of a business organisation is prepared to know
the net profit or loss made by the
organisation during the year, whereas income and expenditure account of a
non-profit organisation is prepared to know the surplus
(excess of income over expenditure) or deficiency
(excess of expenditure over income) at the end of the year.
4.
In case of the business organisation there is proprietor’s
capital which appears in the liability side of the balance
sheet, whereas in case of the non-profit organisation there is no such
proprietor’s capital. In fact, in case of the non-profit organisation there is capital fund which also appears in the
liability side of the balance sheet.
Difference
between Receipts and Payments Account and Income and Expenditure Account:
|
|
Receipts
& Payments A/c |
Income
& Expenditure A/c |
|
1 |
It is a summarised Cash Book |
It closely resembles the P/L A/c of a Trading concern. |
|
2 |
Receipts are debited and Payments are credited. |
Incomes are credited and Expenditures are debited. |
|
3 |
Transactions are recorded on Cash basis. |
Transactions are recorded on Accrual Basis |
|
4 |
Receipts and payments related to previous period and
future period are also recorded in this A/c along with receipts and payments
of current period. Outstanding amounts for current period are excluded. |
Incomes and expenditures of current period only are
recorded in this A/c. Outstanding amounts of current period are included. |
|
5 |
It records both Capital and Revenue transactions. |
It records Revenue transactions only. |
|
6 |
It is a Real Account in nature. |
It is a Nominal Account in nature. |
|
7 |
It starts with opening Cash and Bank Balances and
ends with closing Cash and Bank Balances. |
It does not record such balances; rather its final
balance shows a surplus or a deficit for the period. |
|
8 |
It does not record notional loss or non-cash expenses like bad debts, depreciations etc. |
It considers all such expenses for matching against revenues |
|
9 |
Its closing balance is carried forward to the same
A/c of the next period. |
Its closing balance is transferred to the Capital
Fund or General Fund or Accumulated Fund of the same
period’s B/S. |
|
10 |
It helps to prepare an Income & Expenditure A/c. |
It helps to prepare a Balance Sheet. |
Definition, meaning and accounting treatment
of some important items
CAPITAL
FUND
Capital
fund may be assumed to be the capital of non-profit organisation. It
represents:
(a)
Amount contributed by the supporters, members and well-wishers of the
organisation in cash or kind in the form of non-recurring general purpose donations;
(b)
Part of the entrance fees received from the members which have been
capitalised; and
(c)
Surplus (excess of income over expenditure) generated during the year.
If there is any deficiency (excess of expenditure over
income) at the end of the year it is deducted from the capital fund. Capital
fund (also known as general fund or accumulated fund) is shown in the liability
side of the balance sheet.
DONATION
It is the
amount contributed by the supporters, members and well-wishers of the
organisation in cash or kind. The donations may be
special purpose donations or general donations. Examples of special purpose donations are donations
received for prize, building, tournament, library, etc.
Special purpose donations are to be treated as capital
receipts and accordingly should be credited
to the particular fund for which the amount has been donated and should be
shown in the liability side of the balance sheet.
General donations may be of two types: non-recurring
and recurring. Non-recurring
donations received should be credited to Capital Fund, whereas recurring
donations received should be credited to Income & Expenditure Account.
LEGACY
It is an amount or other item of value received from a
deceased person under the terms of a will. It is directly added
to capital fund. If a legacy is received for any special
purpose, it should be credited to the particular fund for which the amount of
legacy has been received.
SUBSCRIPTIONS
It is the amount paid by the members at regular
intervals (monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or yearly) to keep their membership
alive. It is treated as income and credited to the
income and expenditure account of the period concerned.
LIFE
MEMBERSHIP FEE
It is a lump sum payment made by a member of an
organisation in order to become a life member of the organisation. There are
two alternative accounting treatments for the life membership fee.
Alternative: I
The entire amount of life membership fee received is credited to the capital fund.
Alternative:
II
The amount of life membership fee received is credited
to a special fund called life membership
fund and an amount equal to the annual subscription is
transferred every year to the income and expenditure account, the balance of
the fund being carried forward till it is fully exhausted. If any life member
dies before the entire amount paid by him has been transferred to the income
and expenditure account in the above way, the balance should be transferred to
the capital fund on the date of his death. In the absence of
any specific instruction in regard to which alternative treatment is to be
followed, the first alternative treatment should be followed.
ENTRANCE/ADMISSION
FEE
It is the fee paid by a member at the time of becoming
a member. It is paid by the member only once in life time for becoming a
member. In the absence of any specific instruction
entrance fee received should be treated as capital receipt and accordingly
credited to the capital fund. When
a specific direction has been given as to how much of the entrance fee received
should be treated as capital receipt and how much as revenue receipt, it should
be treated accordingly.
HONORARIUM
It is a token payment made to a person who has
voluntarily undertaken a service which would normally command a fee. It is thus
an expression of gratitude rather than a payment for the work done. It is treated as expense and debited to the income and
expenditure account of the period concerned.
SPECIAL
FUND
It is a fund set up for a special purpose. For
example, a cricket club may wish to organise annual cricket tournaments and may
set up a special fund for this purpose (may be by the name of “Tournament Fund”).
It should be noted that all the amounts received as donations or by fund
raising activities and all incomes relating to the special fund should be
credited to the special fund. Similarly, all expenses relating to the special
fund should be debited to the special fund. A special fund appears in the
liabilities side of the balance sheet. If the Special Fund is used to purchase
a fixed asset, the cost of the asset should be transferred from the Special
Fund to the Capital Fund by the following journal entry:
|
Date |
Particulars |
|
Debit (Rs) |
Credit (Rs) |
|
1 |
Special Fund A/c |
Dr |
|
|
|
|
To Capital Fund A/c |
|
|
|
|
|
(Cost of fixed asset
purchased transferred from the Special Fund to the Capital Fund) |
|
|
|
Accounting Treatment of Some Important Items
(Tabular Presentation):
|
ITEMS |
INCOME AND EXPENDITURE ACCOUNT |
BALANCE SHEET |
|
1. Donation |
|
|
|
Special
purposes donation |
|
Taken to balance sheet and added to the special fund
in the liability side |
|
General
donation |
|
|
|
Recurring |
Credited to I/E Account |
|
|
Non-recurring |
|
Credited to capital fund (i.e. added to capital
fund) |
|
2. Legacy |
|
Added to capital fund |
|
3. Subscription |
Credited to I/E Account |
|
|
4. Life Membership Fee |
|
|
|
1st
Alternative |
|
Credited to capital fund |
|
2nd
Alternative (by opening Life Membership Fund)
Note: In the absence of specific instruction about which
alternative is to be followed, always the first alternative should be
followed |
Every year total subscription of the year will be deducted
from the Life Membership Fund and will be credited to the I/E Account |
Credited to Life Membership Fund in the liabilities
side of the Balance Sheet
On death of a member, the balance left, if any, out
of his Life Membership Fee should be transferred to the Capital Fund from the
Life Membership Fund |
|
5. Entrance fee / Admission
fee |
If there is any specific instruction to treat a part
of the entrance fee as revenue receipt, that part of entrance fee should be
credited to I/E A/c. |
In the absence of any specific instruction, entrance
fee should be credited to capital fund in the Balance Sheet as capital
receipt.
|
|
6. Honorarium |
Treated as an expense and debited to I/E A/c |
|
|
7. Special fund /
Endowment fund [Examples: Tournament fund, prize fund, cultural
program fund, etc.] |
|
It is shown in the liability side of balance sheet.
All expenses relating to the special fund should be deducted from the special
fund and all incomes relating to the special fund should be added to the
special fund in the Balance Sheet.
If any fixed asset is purchased by using special
fund, cost of such asset should be transferred to capital fund from the special
fund. |
How to
calculate ‘income from subscriptions’ when ‘subscriptions received’ is given:-
Computation of income from subscriptions
|
|
Particulars |
Rs |
Rs |
|
|
Subscriptions received |
|
××× |
|
A: |
Outstanding subscriptions at the end of the year |
××× |
|
|
A: |
Subscriptions received in advance at the beginning
of the year |
××× |
|
|
A: |
Subscriptions written off during the year |
××× |
××× |
|
|
|
|
××× |
|
L: |
Outstanding subscriptions at the beginning of the
year |
××× |
|
|
L: |
Subscriptions received in advance at the end of the
year |
××× |
××× |
|
|
Income from subscriptions (Credited to the Income and Expenditure Account) |
|
××× |
How to
calculate ‘subscriptions received’ when ‘income from subscriptions’ is given:-
Computation of subscriptions received
|
|
Particulars |
Rs |
Rs |
|
|
Income from subscriptions |
|
××× |
|
A: |
Outstanding subscriptions at the beginning of the
year |
××× |
|
|
A: |
Subscriptions received in advance at the end of the
year |
××× |
××× |
|
|
|
|
××× |
|
L: |
Outstanding subscriptions at the end of the year |
××× |
|
|
L: |
Subscriptions received in advance at the beginning
of the year |
××× |
|
|
L: |
Subscriptions written off during the year |
××× |
××× |
|
|
Subscriptions received (Debited to the Receipts and Payments Account) |
|
××× |
Subscription
Account
‘Income from subscriptions’ and ‘Subscriptions
received’ can also be calculated as balancing figures by preparing Subscription
Account as follows:
Format of
Subscription Account in PDF
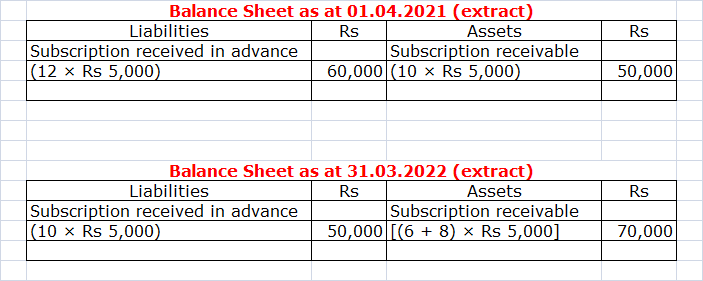
Example:
There are 100 members in a club. Subscription per
member per annum is Rs 5,000. For the current accounting year 2021-2022, 8
members could not pay their subscriptions, whereas 12 members paid their
current year’s subscriptions in the previous year. 10 members could not pay
their previous year’s subscriptions out of which 4 members cleared their dues
during the current year. 10 members paid their next year’s subscriptions during
the current year in advance.
Prepare
1.
Receipts and Payments A/c for the year ended 31.03.2022 (extracts);
2.
Income and Expenditure A/c for the year ended 31.03.2022 (extracts);
3.
Balance Sheet as at 1st April, 2021 (extracts); and
4.
Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2022 (extracts).
Solution to Example
Part B
Financial Accounting
Accounting for
Non-Profit Organisation
Selected Problems and Solutions
Illustration:
1
The following summary of the Cash Book for the year 2012-13 has been
prepared by the treasurer of a club:
|
Receipts |
Rs |
Payments |
Rs |
|
To Balance b/d [As on 01.04.2012] |
4,740 |
By Wages |
13,380 |
|
To Subscriptions |
29,720 |
By Restaurant Purchases |
50,400 |
|
To Entrance Fees |
3,200 |
By Rent (For 18 months’ up to 30th June, 2,013) |
7,500 |
|
To Restaurant Receipts |
56,800 |
By Rates |
2,700 |
|
To Games and Competition Receipts |
13,640 |
By Secretary’s Salary |
3,120 |
|
To Due to Secretary for Petty Exp. |
80 |
By Lighting |
7,200 |
|
|
|
By Competition Prizes |
4,000 |
|
|
|
By Printing and Postage |
6,000 |
|
|
|
By Fixed Deposit |
8,000 |
|
|
|
By Balance c/d [As on 31.03.2013] |
5,880 |
|
|
1,08,180 |
|
1,08,180 |
On April 1, 2012
the club’s assets were: Furniture Rs 48,000, Restaurant stock Rs 2,600; Stock
of prizes Rs 800; Rs 5,200 was outstanding for supplies to the restaurant.
On March, 31, 2013,
the Restaurant stocks were Rs 3,000 and prizes in hand were Rs 500, while the
club owed Rs 5,600 for restaurant supplies.
It was also found
that subscriptions unpaid at March 31, 2013 amounted to Rs 1,000 and that the
figure of Rs 29,720 shown in the Cash Book included Rs 700 in respect of
previous year and Rs 400 paid in advance for the following year.
Prepare an account
showing the Profit or Loss made on the Restaurant and a General Income and
Expenditure Account for the year ended 31.3.2013 together with a Balance Sheet
as at that date after writing 10% off the Furniture.
Illustration:
2
‘Citizen Club’ was
registered in a city and the accountant prepared the following Receipts and
Payments Account for the year ended 31st Dec., 2013 and showed a
deficit of Rs 14,520:
|
|
(Rs) |
(Rs) |
|
Receipts: |
|
|
|
Subscriptions |
62,130 |
|
|
Fair Receipts |
7,200 |
|
|
Variety Show
Receipts (net) |
12,810 |
|
|
Interest |
690 |
|
|
Bar Collection |
22,350 |
|
|
Cash spent more |
1,000 |
1,06,180 |
|
Payments: |
|
|
|
Premises |
30,000 |
|
|
Honorarium to
Secretary |
12,000 |
|
|
Rent |
2,400 |
|
|
Rates and Taxes |
3,780 |
|
|
Printing and
Stationery |
1,410 |
|
|
Sundry Expenses |
5,350 |
|
|
Wages |
2,520 |
|
|
Fair Expenses |
7,170 |
|
|
Bar Purchase
Payments |
17,310 |
|
|
Repairs |
960 |
|
|
New Car (less
proceeds of old car Rs 9,000) |
37,800 |
1,20,700 |
|
Deficit |
|
14,520 |
The additional
information available is:
|
|
01.01.2013 |
31.12.2013 |
|
|
(Rs) |
(Rs) |
|
Cash in hand |
450 |
– |
|
Bank balance as
per pass book |
24,690 |
10,440 |
|
Cheques issued
but not presented for s/expenses |
270 |
90 |
|
Subscription due |
3,600 |
2,940 |
|
Premises at cost |
87,000 |
1,17,000 |
|
Accumulated
depreciation on premises |
56,400 |
– |
|
Car at cost |
36,570 |
46,800 |
|
Accumulated
depreciation on car |
30,870 |
– |
|
Bar Stock |
2,130 |
2,610 |
|
Creditors for Bar
Purchases |
1,770 |
1,290 |
Cash overspent
represents honorarium to secretary not withdrawn due to Cash deficit. His
annual honorarium is Rs 12,000. Depreciation on premises and car is to be
provided at 5% and 20% on written-down value.
You are required to
prepare the correct Receipts and Payments Account, Income and Expenditure
Account and Balance Sheet as at 31st Dec., 2013.
Illustration: 3
From the following
Trial Balance prepare Income & Expenditure A/c for the year ended
31-12-2013 and the balance sheet as on 31-12-2013 in the books of an Aryan
Education Society.
Trial Balance
|
Particulars |
Debit (Rs) |
Credit (Rs) |
|
Library Books |
2,30,000 |
|
|
Purchase of
Library Books |
52,200 |
|
|
Furniture |
1,59,500 |
|
|
Purchase of
Furniture |
35,500 |
|
|
Buildings |
37,89,000 |
|
|
Investments |
21,25,000 |
|
|
Creditors |
|
1,77,900 |
|
Debtors |
59,700 |
|
|
Investment
Reserve Fund |
|
1,85,000 |
|
Entrance Fees |
|
2,02,600 |
|
Examination Fees |
|
32,500 |
|
Certificate Fees |
|
7,800 |
|
Subscriptions
Received |
|
2,75,800 |
|
Hire Charges |
|
95,500 |
|
Interest |
|
85,000 |
|
Other Receipts |
|
4,400 |
|
Salary |
1,55,900 |
|
|
Printing and
Stationery |
8,500 |
|
|
Postage and
Telephone |
2,500 |
|
|
Insurance |
10,400 |
|
|
Examination
Expenses |
24,000 |
|
|
Periodicals |
15,600 |
|
|
Prizes Fund |
|
2,15,000 |
|
Prizes Fund Investments |
2,10,400 |
|
|
Prizes Investment
Income |
|
10,200 |
|
Prizes Given |
9,500 |
|
|
Prizes Bank
Balance |
2,450 |
|
|
Donations
(capital) |
|
1,99,000 |
|
General Expenses |
5,250 |
|
|
Capital Fund |
|
54,71,720 |
|
Bank Balance |
65,500 |
|
|
Cash in Hand |
1,520 |
|
|
Total |
69,62,420 |
69,62,420 |
Additional
information:
Subscription
receivable Rs 22,500, subscription received for 2014 Rs 7,850, Interest accrued
on investments Rs 6,250, salary outstanding for 2013 Rs 12,500, Prepaid
insurance Rs 4,500.
Depreciate Books @
15%, Building @ 1% and Furniture @ 10%.
Illustration:
4
From the following
Receipts and Payments Account prepare an Income and Expenditure Account for the
year ended 31.12.2016.
Receipts and Payments A/c
For the year ended
31.12.2016
|
Receipts |
Rs. |
Payments |
Rs. |
|
To Balance b/d: |
|
By Purchase of
furniture |
10,000 |
|
Cash in hand |
1,200 |
By Rent |
3,600 |
|
Cash at bank |
3,400 |
By Honorarium |
4,000 |
|
To Subscriptions |
24,500 |
By Salaries |
2,100 |
|
To Entrance Fees |
3,000 |
By Sports Exp. |
4,700 |
|
|
|
By Sundry Exp. |
1,100 |
|
|
|
By Printing and
Stationery |
800 |
|
|
|
By Balance c/d: |
|
|
|
|
Cash in hand |
1,700 |
|
|
|
Cash at bank |
4,100 |
|
|
32,100 |
|
32,100 |
Additional information:
|
|
31.12.2015 |
31.12.2016 |
|
|
(Rs) |
(Rs) |
|
Subscription due |
2,100 |
3,200 |
|
Subscription
received in advance |
1,400 |
2,700 |
|
Rent outstanding |
600 |
300 |
|
Salaries paid in
advance |
1,200 |
900 |
|
Furniture |
18,000 |
23,000 |
60 % of the
entrance fees are to be capitalized. Interest on savings bank account for Rs 280
has not been entered in the cash book. Old furniture (WDV Rs 8,000) was exchanged
at an agreed price of Rs 5,000 for a new furniture costing Rs 15,000.
Illustration:
5
The following
information was obtained from the books of Young Bengal Club as on 31-03-2013
at the end of first year of the club. Prepare the Receipts & Payments A/c,
Income & Expenditure A/c and Balance sheet of the club.
(1) Donations received
for Building & Books – Rs 2,00,000
(2) Other revenue
incomes and receipts were:
|
|
Incomes |
Receipts |
|
Entrance Fees |
17,000 |
17,000 |
|
Subscriptions |
20,000 |
19,000 |
|
Locker Rent |
600 |
600 |
|
Sundry Income |
1,600 |
1,060 |
|
Refreshment A/c |
Nil |
16,000 |
(3) Other revenue
expenditure and actual payments were:
|
|
Expenses |
Payments |
|
Land (Cost: Rs 10,000) |
Nil |
10,000 |
|
Furniture (Cost: Rs 1,46,000) |
Nil |
1,30,000 |
|
Salaries |
5,000 |
4,800 |
|
Maintenance of play ground |
2,000 |
1,000 |
|
Rent |
8,000 |
8,000 |
|
Refreshment A/c |
Nil |
8,000 |
Donations were
utilized to the extent of Rs 25,000 for buying books, balance were unutilized.
In order to keep it safe, 9% Govt. Securities were purchased on 31-3-2013 for
Rs 1, 60,000. Remaining amount was put in bank as term deposit on 31-3-2013.
Depreciate Furniture and books @ 10% for the whole year.
Illustration:
6
Following is the
Receipts and Payments A/c of Young Indians’ Club for the year ended 31-03-2013.
Receipts and Payments A/c
For the year ended 31.03.2013
|
Receipts |
Rs. |
Payments |
Rs. |
|
To Balance b/d: |
|
By Administrative
exp |
1,25,000 |
|
Cash in hand |
3,000 |
By Programme exp |
2,75,000 |
|
Cash at bank |
7,000 |
By FD with bank |
1,25,000 |
|
To Subscriptions
Received: |
|
By Investment in ICICI Bonds |
3,00,000 |
|
Up to 31.03.2012 |
14,000 |
By Fixed assets |
80,000 |
|
For 2012 – 13 |
1,50,000 |
By Balance c/d: |
|
|
For 2013 – 14 |
16,000 |
Cash in hand |
2,700 |
|
To Advertisements From Programme |
5,00,000 |
Cash at bank |
5,000 |
|
To FD with Bank |
75,000 |
|
|
|
To Interest on
Savings |
700 |
|
|
|
To Interest on FD |
22,000 |
|
|
|
To Sale of
tickets – Programme |
25,000 |
|
|
|
To Matured Govt. Security (Cost: Rs 80,000 and Interest: Rs 8,000) |
1,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
9,12,700 |
|
9,12,700 |
The club informs
you that:
(a)
Membership fee for 2012-13 due is Rs
25,000; and Rs 1,000 from a member who has not yet paid for 2011-12 as well. A
provision needs to be done on this.
(b)
Interest receivable on 31-03-2013 on
ICICI bond is Rs 30,000 and on Govt. Securities is Rs 24,000.
(c)
Prepaid administrative expenses on
31-3-2013 amounts to Rs 7,000.
(d)
Outstanding administrative expenses as
on 31-3-2013 Rs 8,000.
(e)
Depreciation to be provided is Rs 12,500.
(f)
Programme is an annual feature.
The Balance Sheet
as on 31-3-2012 is also provided as below:
Balance Sheet as at
31.03.2012
|
Liabilities |
Rs |
Assets |
Rs |
|
Trust Fund |
5,00,000 |
Cash in hand |
3,000 |
|
Accumulated
surplus |
1,05,000 |
Bank Account |
7,000 |
|
Subscriptions
received in advance |
10,000 |
Fixed Deposit |
2,00,000 |
|
Outstanding
Administrative Exp. |
10,000 |
Govt. Securities |
3,00,000 |
|
|
|
Fixed Assets |
95,000 |
|
|
|
Subscriptions
receivable |
15,000 |
|
|
|
Prepaid
Administrative Exp. |
5,000 |
|
|
6,25,000 |
|
6,25,000 |
Prepare Income and
Expenditure Account and the Closing Balance Sheet for the year 2012-13.
Illustration:
7
The following are
the items of Receipts and Payments of the Bengal Club as summarized from the
books of accounts maintained by the Secretary:
|
Receipts |
Rs |
Payments |
Rs |
|
Opening Balance
as at 1.1.2013 |
4,200 |
Manager’s Salary |
1,000 |
|
Entrance Fees
(2012) |
1,000 |
Printing and
Stationery |
2,600 |
|
Entrance Fees
(2013) |
10,000 |
Advertising |
1,800 |
|
Subscriptions
(2012) |
600 |
Fire Insurance |
1,200 |
|
Subscriptions
(2013) |
15,000 |
Investments
Purchased |
20,000 |
|
Interest Received
on Investments |
3,000 |
Closing Balance
as at 31.12.2013 |
7,600 |
|
Subscriptions
(2014) |
400 |
|
|
|
|
34,200 |
|
34,200 |
It was ascertained
from enquiry that the following represented a fair picture of the Income and
Expenditure of the Club for the year 2013 for audit purpose:
|
Expenditure |
Rs |
Rs |
Income |
Rs |
|
Manager’s Salary |
|
1,500 |
Entrance Fees |
10,500 |
|
Printing and
Stationery |
2,000 |
|
Subscriptions |
15,600 |
|
ADD: Outstanding |
400 |
2,400 |
Interest on Inv. |
4,000 |
|
Advertisement (no outstanding) |
|
1,600 |
|
|
|
Audit Fees |
|
500 |
|
|
|
Fire Insurance |
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
Depreciation |
|
4,940 |
|
|
|
Surplus |
|
18,160 |
|
|
|
|
|
30,100 |
|
30,100 |
You are required to
prepare the Balance Sheet of the Club as on 31.12.2012 and 31.12.2013, it being
given that the values of the Fixed Assets as on 31.12.2012 were: Building Rs
44,000, Cricket Equipment Rs 25,000 and Furniture Rs 4,000. The rates of depreciation
are: Building 5%, Cricket Equipments 10%, and Furniture 6%. (You are entitled
to make assumptions as may be justified.)
Click here for Solution: 7 in PDF
Illustration:
8
The Income and
Expenditure Account of the Calcutta Club is:
Income and Expenditure A/c
For the year ended
31.12.2013
|
Expenditure |
Rs |
Income |
Rs |
|
To Salaries |
1,750 |
By Subscriptions |
2,000 |
|
To General
Expenses |
500 |
By Donation |
1,050 |
|
To Depreciation |
300 |
|
|
|
To Surplus |
500 |
|
|
|
|
3,050 |
|
3,050 |
Adjustments are to
be made in respect of the following:
(1)
Subscription for 2012 unpaid at 1.1.2013
Rs 200; Rs 180 of which was received in 2013.
(2)
Subscription paid in advance at 1.1.2013
Rs 50.
(3)
Subscription paid in advance at
31.12.2013 Rs 40.
(4)
Subscription for 2013 unpaid at
31.12.2013 Rs 70.
(5)
Sundry Asset at the beginning of the
period Rs 2,600; Sundry Asset after depreciation Rs 2,700 at the end of the
period.
(6)
Cash balance at 1.1.2013 Rs 160.
Prepare a Receipts
and Payments Account.
Illustration:
9
Jodhpur Club
furnishes you the Receipts and Payments Account for the year ended 31.03.2013.
|
Receipts |
Rs. |
Payments |
Rs. |
|
To Balance b/d: |
|
By Salary |
20,000 |
|
Cash in hand |
40,000 |
By Repair
expenses |
5,000 |
|
Cash at bank |
1,00,000 |
By Furniture |
60,000 |
|
To Donations |
50,000 |
By Investments |
60,000 |
|
To Subscriptions |
1,20,000 |
By Misc. Expenses |
5,000 |
|
To Entrance Fees |
10,000 |
By Insurance
premium |
2,000 |
|
To Interest on Investments |
1,000 |
By Billiards
Table and other sports items |
80,000 |
|
To Interest from
banks |
4,000 |
By Stationery
exp. |
1,500 |
|
To Sale of old newspaper |
1,500 |
By Drama expenses |
5,000 |
|
To Sale of drama tickets |
10,500 |
By Balance c/d: |
|
|
|
|
Cash in hand |
26,500 |
|
|
|
Cash at bank |
72,000 |
|
|
3,37,000 |
|
3,37,000 |
Additional information:
(i)
Subscription in arrear for 2012-13 is Rs
9,000 and subscription in advance for the year 2013-14 is Rs 3,500.
(ii)
Rs 400 were the insurance premium
outstanding as on 31.03.2012.
(iii)
Miscellaneous expenses prepaid Rs 900.
(iv) 50% of donation is
to be capitalized.
(v)
Entrance fees to be treated as revenue
income.
(vi) 8% interest has
accrued on investments for five months.
(vii) Billiards table and
other sports equipments costing Rs 3,00,000 were purchased in the financial
year 2011-
12 and of which Rs
80,000 were not paid as on 31.03.12. There is no charge for depreciation to be
considered.
You are required to
prepare Income and Expenditure account for the year ended 31.03.13 and Balance Sheet
of the Club as at 31.03.13.
Illustration:
10
The Income and
Expenditure Account of the Bhartia Club for the year ended 31st
March, 2014 is as follows:
|
Expenditure |
Rs |
Income |
Rs |
|
To Salaries |
95,000 |
By Subscriptions |
1,50,000 |
|
To General
Expenses |
20,000 |
By Entrance Fees |
5,000 |
|
To Audit Fee |
5,000 |
By Collection
from Annual Sports |
65,000 |
|
To Printing and Stationery |
9,000 |
|
|
|
To Secretary’s Honorarium |
20,000 |
|
|
|
To Interest |
2,000 |
|
|
|
To Bank Charges |
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Depreciation on Sports Equipment |
6,000 |
|
|
|
To Expenditure on Annual Sports |
50,000 |
|
|
|
To Surplus |
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
2,20,000 |
|
2,20,000 |
Other Information:
|
Expenditure |
Rs |
|
Subscription
outstanding on 31.03.2013 |
12,000 |
|
Subscription
received in advance on 31.03.2013 |
9,000 |
|
Subscription
outstanding on 31.03.2014 |
15,000 |
|
Subscription
received in advance on 31.03.2014 |
5,400 |
|
Salaries
outstanding on 31.03.2013 |
8,000 |
|
Salaries
outstanding on 31.03.2014 |
9,000 |
|
Audit Fee
outstanding on 31.03.2013 |
4,000 |
|
Audit Fee
outstanding on 31.03.2014 |
5,000 |
|
General expenses
prepaid on 31.03.2014 |
1,200 |
|
Sports equipment
as on 31.03.2013 |
52,000 |
|
Sports equipment
after depreciation as on 31.03.2014 |
54,000 |
|
Other balances as on 31.03.2014: |
|
|
Freehold Ground |
2,00,000 |
|
Bank Loan |
40,000 |
|
Cash and Bank |
32,000 |
You are required to
prepare the Receipts and Payments Account for the year ended 31st
March, 2014 and Balance sheet as at 31st March, 2014.
Illustration:
11
Income and Expenditure Account and the Balance Sheet of
Nav Bharat Club are as under:
Income and Expenditure
Account
For the year ending
31.03.2012
|
Expenditure |
Rs |
Income |
Rs |
|
To Upkeep of
Ground |
21,000 |
By Subscriptions |
56,640 |
|
To Printing and Stationery |
2,800 |
By Sale of old newspaper |
530 |
|
To Salaries |
28,000 |
By Lectures |
8,000 |
|
To Depreciation on: |
|
By Entrance Fees |
2,900 |
|
Ground and
Building |
9,000 |
By Misc. Incomes |
1,200 |
|
Furniture |
1,000 |
|
|
|
To Repairs |
3,500 |
|
|
|
To Surplus |
3,970 |
|
|
|
|
69,270 |
|
69,270 |
Balance Sheet as at
31.03.2012
|
Liabilities |
Rs |
Rs |
Assets |
Rs |
|
Capital Fund: |
|
|
Ground and Building |
1,43,200 |
|
Opening balance |
1,56,430 |
|
Furniture |
9,000 |
|
ADD: Surplus |
2,900 |
|
Sports Prize Fund Inv. |
43,000 |
|
ADD: Entrance Fee |
3,970 |
1,63,300 |
Subscriptions receivable |
2,600 |
|
Sports Prize Fund: |
|
|
Cash and Bank |
19,400 |
|
Opening balance |
51,000 |
|
|
|
|
ADD: Interest |
4,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
55,500 |
|
|
|
|
LESS: Prizes |
6,500 |
49,000 |
|
|
|
Outstanding
salary |
|
4,200 |
|
|
|
Subscription recd in advance |
|
700 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,17,200 |
|
2,17,200 |
The following
adjustments have been made in the above accounts:
(i)
Upkeep of ground Rs 1,500 and printing
and stationery Rs 510 relating to 2010-2011 was paid in 2011-12.
(ii)
One-half of entrance fees have been
capitalized.
(iii)
Subscription outstanding in 2010-11 was
Rs 3,100 and for 2011-12 Rs 2,600.
(iv) Subscription received
in advance in 2010-11 was Rs 1,100 and in 2011-12 for 2012-13 Rs 700.
(v)
Outstanding salary on 31.03.2011 was Rs 3,600.
Prepare Receipts
& Payments Account for the year ended on 31st March, 2012.
Click here for Solution: 11 in PDF



No comments:
Post a Comment