(Formulas and Selected Problems and Solutions)
Part A:
In Part A you will find Formulas of different measures of Dispersion including the important properties of standard deviation.
Part B:
In Part B you will find seventeen selected problems with solutions.
A measure of
dispersion is designed to state numerically the extent to which individual
observations vary around the average. There are several measures of dispersion
under the two broad categories as follows:
A.
Absolute
Measures:
1.
Range,
2. Quartile Deviation
(Also known as 'Semi-Interquartile Range')
3.
Mean
Deviation About Mean,
4.
Mean
Deviation About Median, and
5.
Standard
Deviation.
B.
Relative
Measures:
1.
Coefficient
of Range
2.
Coefficient
of Quartile Deviation,
3.
Coefficient
of M.D. About Mean,
4.
Coefficient
of M.D. About Median, and
5.
Coefficient
of Variation.
Note: Mean
Deviation (M.D.) is usually calculated about arithmetic mean, and hence if it’s
only ‘Mean Deviation’, it refers to M.D. About Mean only.
Formulas
1.
Range
=
Largest Value (L) – Smallest Value (S)
2.
Coefficient
of Range
=
[(L – S) ÷ (L + S)] × 100
3.
Quartile
Deviation = ½ (Q3 – Q1)
4. Coefficient
of Quartile Deviation (1st Formula)
=
[(Q3 – Q1) ÷ (Q3 + Q1)] × 100
5. Coefficient
of Quartile Deviation (2nd Formula)
=
[Quartile Deviation ÷ Median) × 100
6. Mean
Deviation About Mean (For Simple Distribution)
=
[∑Mod (xi – Mean)] ÷ n
7.
Mean
Deviation About Mean (For Frequency Distribution)
=
[∑fi {Mod (xi – Mean)}] ÷ ∑fi
8. Mean
Deviation About Median (For Simple Distribution)
=
[∑Mod (xi – Median)] ÷ n
9. Mean
Deviation About Median (For Frequency Distribution)
=
[∑fi {Mod (xi – Median)}] ÷ ∑fi
10.
Coefficient
of M.D. About Mean
=
[M.D. About Mean ÷ Mean] × 100
11.
Coefficient
of M.D. About Median
=
[M.D. About Median ÷ Median] × 100
=
[∑{(xi – Mean)2} ÷ n](1/2)
2.
For
Simple Distribution (2nd Formula – Direct Method)
= [{∑(xi2)
÷ n} – {(∑xi ÷ n)2}](1/2)
3.
For
Simple Distribution (3rd Formula – Short-Cut Method)
= [{∑(di2)
÷ n} – {(∑di ÷ n)2}](1/2)
[Here,
di = xi – A; A = Assumed Mean (as near as possible to the
true mean)]
4.
For
Simple Distribution (4th Formula – Step-Deviation Method)
= [{∑(Di2)
÷ n} – {(∑Di ÷ n)2}](1/2) × c
[Here,
Di = (xi – A)/c; A = Assumed Mean (as near as possible to
the true mean); c = Common factor]
5.
For
Frequency Distribution (1st Formula)
= [∑{fi(xi
– Mean)2} ÷ ∑fi](1/2)
6.
For
Frequency Distribution (2nd Formula – Direct Method)
= [{∑fi(xi2)
÷ ∑fi} – {(∑fixi ÷ ∑fi)2}](1/2)
7.
For
Frequency Distribution (3rd Formula – Short-Cut Method)
= [{∑fi(di2)
÷ ∑fi} – {(∑fidi ÷ ∑fi)2}](1/2)
[Here,
di = xi – A; A = Assumed Mean (value of that observation
or that mid-value which has the highest frequency)]
8.
For
Frequency Distribution (4th Formula – Step-Deviation Method)
= [{∑fi(Di2)
÷ ∑fi} – {(∑fiDi ÷ ∑fi)2}](1/2)
× c
[Here,
Di = (xi – A)/c; A = Assumed Mean (value of that
observation or that mid-value which has the highest frequency); c = Common
factor or common width]
9. Coefficient of Variation (i.e. Coefficient of SD)
= (SD ÷ AM) × 100
10.
Variance
= SD2
Important note:
Formula of SD
for simple frequency distribution and grouped frequency distribution under all
the above four methods are same. Only thing to be remembered is that in case of grouped frequency distribution xi
will be the mid-values of the class intervals.
Important Properties of Standard Deviation
1.
If
y = x ± c where c is a constant,
SD
of y = SD of x
I.e.
σy = σx
2.
If
x = c + dy where c and d are constants,
σx
= (Mod d) × σy
3.
[1/n∑(xi
– Mean of x)2](1/2) ≤ [1/n∑ (xi – A)2](1/2)
whatever be the value of A.
SD of Composite Group
Composite SD =
[(N1σ12 + N2σ22
+ N1d12 + N2d22)
÷ (N1 + N2)] (1/2)
[Here,
xi
= Observations of Group 1
yi
= Observations of Group 2
d1
= Mean of Group 1 – Composite Mean
d2
= Mean of Group 2 – Composite Mean
σ1
= SD of Group 1
σ2
= SD of Group 2
Composite mean
= [(∑fx) + (∑fy)]/ (N1 + N2)
= [(N1*Mean of
x) + (N2*Mean of y)]/ (N1 + N2)
N1 = Total
frequency of Group- 1
N2 = Total
frequency of Group- 2]
Statistics
Measures of Dispersion
Selected Problems and Solutions
Problem: 1
Calculate
Standard Deviation and Coefficient of S.D. for the following data:
|
x |
f |
|
2 |
5 |
|
4 |
15 |
|
6 |
20 |
|
8 |
25 |
|
10 |
25 |
|
12 |
20 |
|
15 |
8 |
Solution: 1
Problem: 2
From the
following frequency distribution calculate S.D. and Variance:
|
Annual
Salary (Rs ’000) |
No.
of people |
|
700
– 799 |
4 |
|
800
– 899 |
7 |
|
900
– 999 |
8 |
|
1000
– 1099 |
10 |
|
1100
– 1199 |
12 |
|
1200
– 1299 |
17 |
|
1300
– 1399 |
13 |
|
1400
– 1499 |
10 |
|
1500
– 1599 |
9 |
|
1600
– 1699 |
7 |
|
1700
– 1799 |
2 |
|
1800
– 1899 |
1 |
Solution: 2
Problem: 3
Calculate the
population variance for the following set of grouped data:
|
Class |
Frequency |
|
0
– 199 |
8 |
|
200
– 399 |
13 |
|
400
– 599 |
20 |
|
600
– 799 |
12 |
|
800
– 999 |
7 |
Solution: 3
Problem: 4
Calculate the
mean deviation from the following data, relating to heights (to the nearest
inch) of 100 children:
|
Height
(inches) |
No.
of Children |
|
60 |
2 |
|
61 |
0 |
|
62 |
15 |
|
63 |
29 |
|
64 |
25 |
|
65 |
12 |
|
66 |
10 |
|
67 |
4 |
|
68 |
3 |
Solution: 4
Problem: 5
Find the
standard deviation for the distribution given below:
|
x |
Frequency |
|
1 |
10 |
|
2 |
20 |
|
3 |
30 |
|
4 |
35 |
|
5 |
14 |
|
6 |
10 |
|
7 |
2 |
Solution: 5
Problem: 6
Find the mean
and the S.D. from the following frequency distribution:
|
Weight
(lbs.) |
Number
of Persons |
|
131
– 140 |
2 |
|
141
– 150 |
5 |
|
151
– 160 |
4 |
|
161
– 170 |
9 |
|
171
– 180 |
7 |
|
181
– 190 |
5 |
|
191
– 210 |
3 |
|
211
– 240 |
1 |
Solution: 6
Problem: 7
Find mean deviation
for the following frequency distribution:
|
Variable |
Frequency |
|
3 |
2 |
|
5 |
7 |
|
7 |
10 |
|
9 |
9 |
|
11 |
5 |
|
13 |
1 |
Solution: 7
Problem: 8
Find the S.D.
from the following table giving the age distribution of 540 members of a
Parliament:
|
Age
in Years |
No.
of Members |
|
30 |
64 |
|
40 |
132 |
|
50 |
153 |
|
60 |
140 |
|
70 |
51 |
Solution: 8
Problem: 9
Find the S.D.
from the following frequency distribution:
|
Weight
(lbs.) |
No.
of Boys |
|
120
– 124 |
12 |
|
125
– 129 |
25 |
|
130
– 134 |
28 |
|
135
– 139 |
15 |
|
140
– 144 |
12 |
|
145
– 149 |
8 |
Solution: 9
Problem: 10
Find the
standard deviation of the following distribution:
|
Turnover
(Rs ’000 p.a.) |
No.
of Firms |
|
50
– 100 |
5 |
|
100
– 150 |
8 |
|
150
– 200 |
9 |
|
200
– 250 |
12 |
|
250
– 300 |
18 |
|
300
– 350 |
23 |
|
350
– 400 |
17 |
Solution: 10
Problem: 11
Compute the
S.D. of income from the following distribution:
|
Income
(Rs) |
No.
of Earners |
|
Below
200 |
25 |
|
200
– 399 |
72 |
|
400
– 599 |
47 |
|
600
– 799 |
22 |
|
800
– 999 |
13 |
|
1000
– 1199 |
7 |
Solution: 11
Problem: 12
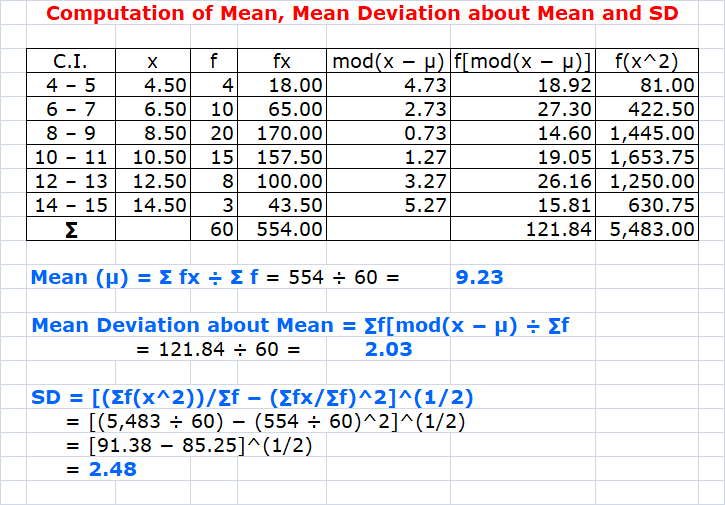
Compute the
arithmetic mean, mean deviation about the mean and standard deviation for the
following data:
|
Scores |
Frequency
(f) |
|
4
– 5 |
4 |
|
6
– 7 |
10 |
|
8
– 9 |
20 |
|
10
– 11 |
15 |
|
12
– 13 |
8 |
|
14
– 15 |
3 |
Solution: 12
Problem: 13
From the
market prices of shares x and y below find out which is more stable in value:
|
x |
y |
|
35 |
108 |
|
54 |
107 |
|
52 |
105 |
|
53 |
105 |
|
56 |
106 |
|
58 |
107 |
|
52 |
104 |
|
50 |
103 |
|
51 |
104 |
|
49 |
101 |
Solution: 13
Problem: 14
You are given the
distribution of wages in two factories X and Y as follows:
|
Wages
(Rs) |
No.
of Workers (X) |
No.
of Workers (Y) |
|
50
– 100 |
2 |
6 |
|
100
– 150 |
9 |
11 |
|
150
– 200 |
29 |
18 |
|
200
– 250 |
54 |
32 |
|
250
– 300 |
11 |
27 |
|
300
– 350 |
5 |
11 |
State in which
factory the wages are more variable.
Solution: 14
Problem: 15
Calculate the
Coefficient of Variation from the following data, showing Grades of 100
students in M.A. Mathematics.
|
Grades |
No.
of Students |
|
30
– 39 |
2 |
|
40
– 49 |
3 |
|
50
– 59 |
11 |
|
60
– 69 |
20 |
|
70
– 79 |
32 |
|
80
– 89 |
25 |
|
90
– 99 |
7 |
Solution: 15
Problem: 16
The Mean and
the S.D. of a sample of 100 observations were calculated as 40 and 5.1
respectively, by a student who by mistake took one observation as 50 instead of
40. Calculate the correct Mean and S.D.
Solution: 16
Problem: 17
For a
distribution of 280 observations mean and standard deviation were found to be
54 and 3 respectively. On checking it was discovered that two observations,
which should correctly read as 62 and 82, had been wrongly recorded as 64 and
80 respectively. Calculate the correct values of mean and standard deviation.
Solution: 17

















No comments:
Post a Comment